
LAVA HERON
The lava heron or Galapagos heron inhabits the intertidal zone and the mangrove areas, feeding at the open shoreline by slowly moving in the shallow waters or even diving into them. Apart from crab and fish, it also eats insects, lizards, and eggs. Its dark shades of gray help them to blend in with the rocks in order to hunt.
Males and females look similar, their feet, head, and eyes get brighter tones in courtship time and it is an opportunistic breeder. The mating months are September to March where females and males create a loud sound, show aerial displays and chase other herons in order to get a monogamous partner. They lay from 1 to 3 eggs in random safe areas of the lowlands around mangrove trees, that take around 22 days to hatch. They protect their territory by chasing intruders and making loud noises.
Due that their meals are on the ground, this bird prefers to walk instead of flying. They can be spotted walking or jumping along their feeding areas, found in all islands.
OTHER SHOREBIRDS
01 Lava Heron
Yes
Endemic
Shorebirds
Animal group
Butorides Sundevalli
Scientific name
45 cm
Animal average size
190-235 g
Animal average weigth





Where to spot this animal?
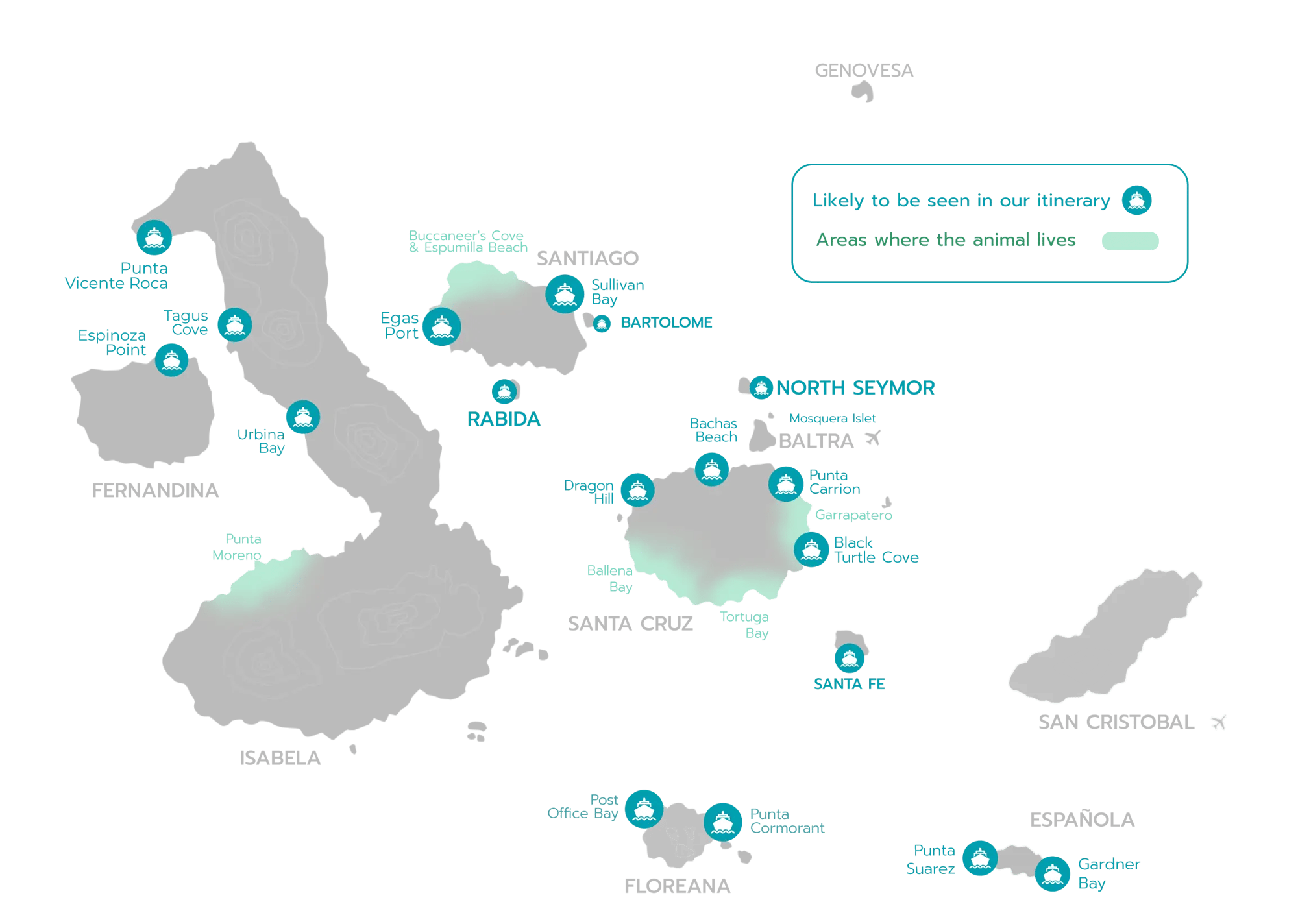
Expeditions where you can find this animal

NORTH EXPEDITION (A)
Visitor sites:

WEST EXPEDITION (B)
Visitor sites:

EAST EXPEDITION (C)
Visitor sites:

SOUTH EXPEDITION (D)
Visitor sites:

NORTH EXPEDITION (A)
Visitor sites:

WEST EXPEDITION (B)
Visitor sites:

EAST EXPEDITION (C)
Visitor sites:






